Introduction
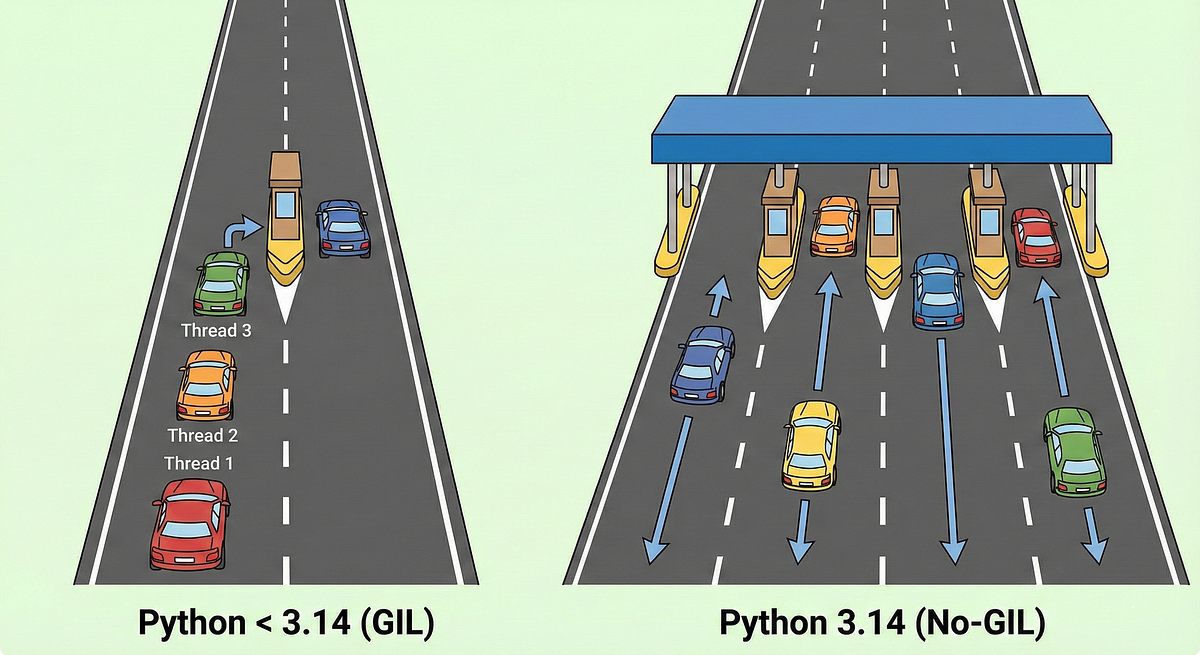
Python 3.14.0 represents a monumental shift in the Python ecosystem, specifically addressing the long-standing Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) that historically limited multi-core performance. This release introduces experimental “free-threading” mode, allowing true parallel execution without the GIL, which is a game-changer for AI workloads. Designed for AI engineers, data scientists, and performance-critical developers, it promises significant speedups for multi-threaded applications. It also introduces new security features aimed at preventing common vulnerabilities, making it essential for production-grade AI systems.
Key Features and Capabilities
The flagship feature is the experimental “free-threading” mode, enabled via a new configure flag. This removes the GIL, allowing Python threads to run simultaneously on multiple CPU cores, unlocking true parallelism for CPU-bound tasks. Previously, the GIL forced even multi-threaded code to run mostly sequentially. Another major addition is the new “safe” string formatting with `str.format` and f-strings receiving security hardening to prevent injection attacks. Additionally, Python 3.14 introduces pattern matching enhancements and improved error messages that are more descriptive, reducing debugging time significantly. For AI engineers, this means frameworks like PyTorch or TensorFlow can leverage native Python parallelism more effectively without relying solely on multiprocessing.
Technology and Implementation
Under the hood, Python 3.14.0 leverages a new memory management model to support free-threading. The C API has been updated to handle thread-safe object access, requiring extensions to be adapted for this mode. The core team has worked on minimizing overhead for single-threaded performance while maximizing gains in multi-threaded scenarios. For security, the interpreter now includes runtime checks for common pitfalls like integer overflows in specific contexts. This version also features a new debugger-friendly “traceback” system that integrates better with IDEs like VS Code. Compared to alternatives like Jython or IronPython, which run on different VMs, CPython 3.14 maintains full compatibility while adding these low-level optimizations.
Use Cases and Practical Applications
In AI development, free-threading enables real-time data preprocessing pipelines to run in parallel without the overhead of spawning separate processes. For instance, an AI engineer building a recommendation system can process multiple data streams simultaneously, reducing latency. In scientific computing, libraries like NumPy can see performance boosts for operations that were previously bottlenecked by the GIL. Real-world applications include high-frequency trading algorithms where Python’s responsiveness is critical. However, users must test extensions for compatibility, as not all third-party packages will immediately support free-threading. This makes it ideal for new projects rather than immediate migrations in legacy systems.
Pricing and Plans
As an open-source language, Python 3.14.0 is completely free to download and use under the PSF License. It is available via python.org, package managers like apt or brew, or through Anaconda distributions. There are no enterprise tiers or hidden costs; all features, including free-threading, are included in the standard release. For cloud deployments, it integrates seamlessly with services like AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Run at no additional Python licensing fee. This contrasts with proprietary alternatives like MATLAB, which require subscriptions, making Python a cost-effective choice for AI teams.
Pros and Cons / Who Should Use It
**Pros:** True parallelism via free-threading boosts performance for multi-core AI tasks; enhanced security features reduce injection risks; improved error messages speed up development; fully open-source with broad ecosystem support.
**Cons:** Free-threading is experimental and may break some existing extensions; potential for race conditions in multi-threaded code requires careful auditing; not all libraries are optimized yet, so adoption may be gradual.
**Who Should Use It:** AI engineers building scalable models, data scientists handling large datasets, and developers prioritizing security in production. It’s less suitable for beginners due to the experimental nature, but ideal for performance-critical teams. Alternatives like Python 3.13 offer stability without free-threading if you need a more conservative upgrade.
Takeaways
– Python 3.14.0 removes the GIL for true multi-core parallelism, ideal for CPU-bound AI workloads.
– New security features like hardened string formatting prevent common vulnerabilities in code.
– Free to use as open-source, with no licensing costs compared to proprietary tools like MATLAB.
– Experimental free-threading requires testing for extension compatibility; best for new projects.
– Improved error messages and pattern matching enhance developer productivity for AI teams.
FAQ
What is the free-threading mode in Python 3.14.0?
Free-threading is an experimental feature that removes the Global Interpreter Lock, allowing multiple threads to run Python code simultaneously on different CPU cores. This is enabled by compiling Python with a specific flag and is designed to improve performance for multi-threaded applications like AI data processing. However, it may not be stable for all workloads yet.
Is Python 3.14.0 free to use for commercial AI projects?
Yes, Python 3.14.0 is completely free and open-source under the Python Software Foundation License. You can use it in commercial applications without any fees, and it integrates with free tools like VS Code and Jupyter for AI development.
How does Python 3.14.0 compare to Python 3.13 for AI workloads?
Python 3.14 builds on 3.13 with experimental free-threading for better parallelism, while 3.13 focuses on stability and incremental improvements. If your AI code is single-threaded, 3.13 might be safer; for multi-core needs, 3.14 offers potential speedups but requires more testing.
What are the main alternatives to Python 3.14.0 for parallel computing?
Alternatives include Jython (for JVM integration) or using multiprocessing in older Python versions, but these add overhead. For true parallelism without GIL, some use Cython or Rust bindings, but Python 3.14 aims to make it native and accessible.
Does Python 3.14.0 improve security for AI code?
Yes, it introduces safer string formatting and runtime checks to prevent injection attacks and overflows, which are common in AI pipelines handling user data. This makes it more secure than previous versions for production AI systems.
How easy is it to upgrade to Python 3.14.0?
Upgrading is straightforward via official installers or package managers, but enabling free-threading needs a custom build. Most code runs unchanged, but test extensions for compatibility. Documentation on python.org provides detailed migration guides.
What support is available for Python 3.14.0?
As open-source, support comes from community forums, Stack Overflow, and official docs. Paid enterprise support is available through companies like Anaconda or Red Hat, but the core is community-driven with regular updates.











How would you rate Python 3.14.0: Ushering in the End of the GIL Era for Secure AI Code?