Takeaways
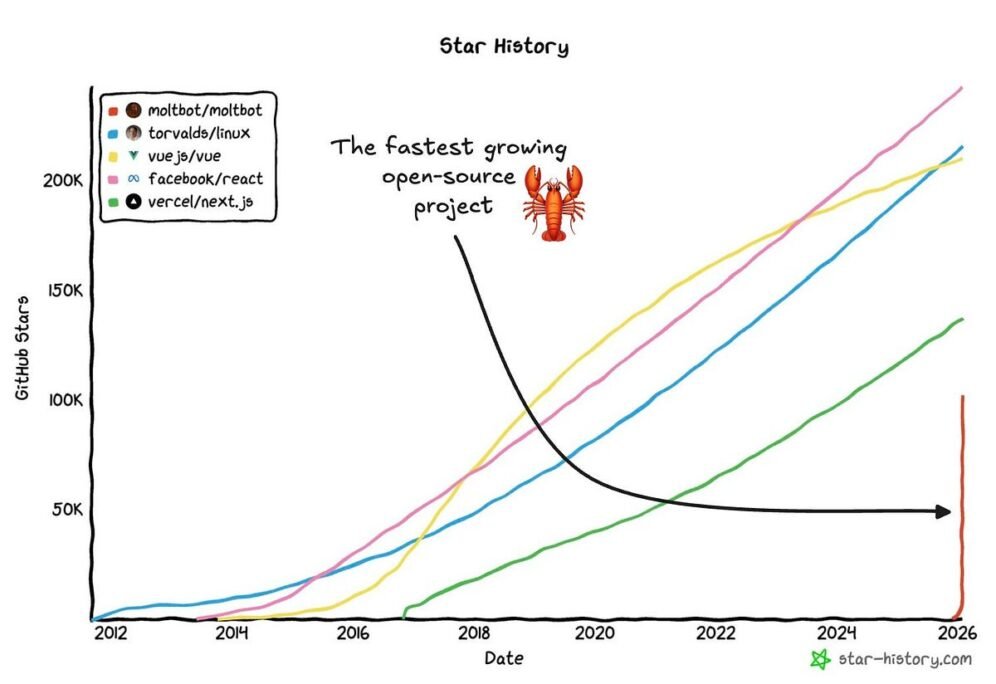
– ClawBot, an AI agent built by a solo developer, reached 100,000 GitHub stars, marking a major milestone for independent AI projects.
– The project’s success highlights a growing demand for accessible, open-source AI tools that can automate complex tasks.
– This achievement challenges the dominance of large tech companies in the AI space, empowering individual developers and small teams.
– The milestone signals a shift toward community-driven AI development and practical, real-world applications.
ClawBot’s Architecture Explains Its Meteoric Rise to 100K GitHub Stars
ClawBot, an autonomous AI agent developed by a single programmer, has surpassed 100,000 stars on GitHub. This milestone was reached on the project’s repository, showcasing significant community interest and adoption. The agent is designed to automate web-based tasks, and its architecture focuses on combining large language models with structured planning for reliable execution. The project’s rapid growth underscores the increasing accessibility of AI development tools and the strong market appetite for practical, open-source automation solutions.
Core Architecture and Technical Approach
ClawBot’s design prioritizes modularity and efficiency, allowing it to handle diverse web tasks effectively. The architecture separates reasoning from execution to improve reliability.
**Key Architectural Components:**
– **Planning Module:** Uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to break down complex user requests into executable steps.
– **Execution Engine:** Translates abstract plans into concrete browser actions like clicking, typing, and navigating.
– **State Management:** Maintains a real-time representation of the web page’s Document Object Model (DOM) to adapt to dynamic content.
– **Error Handling:** Implements feedback loops where the agent can analyze failures and adjust its strategy autonomously.
**Performance and Reliability:**
– **High Success Rates:** The structured planning approach reduces common AI hallucination errors during web interaction.
– **Cost Efficiency:** Optimized token usage minimizes API costs compared to brute-force LLM queries.
– **Scalability:** The architecture supports running multiple agents concurrently for batch task automation.
Why This Milestone Matters for the AI Community
Reaching 100,000 stars is a significant benchmark for any open-source project, but it holds particular weight in the AI sector. It validates the viability of smaller, independent projects competing with corporate-backed initiatives.
**Impact on Development:**
– **Democratization of AI:** Proves that sophisticated AI agents can be built and maintained without massive funding.
– **Community Validation:** High star counts indicate robust user engagement and a willingness to contribute to the codebase.
– **Market Signal:** Suggests a strong demand for automation tools that are transparent, customizable, and free from vendor lock-in.
**Future Implications:**
– **Accelerated Innovation:** The open-source nature allows developers worldwide to improve the core algorithms.
– **Commercial Opportunities:** Successful open-source projects often spawn commercial support services or enterprise forks.
– **Standard Setting:** ClawBot’s architecture could influence how future AI agents are designed for web interaction.
What’s Next for ClawBot and Open Source AI
The project is currently entering a phase focused on stability and community integration. The developer has outlined a roadmap that prioritizes user feedback and feature expansion.
**Upcoming Developments:**
– **Plugin System:** Allowing third-party developers to extend the agent’s capabilities with custom modules.
– **Enhanced Multimodality:** Plans to integrate vision capabilities for handling image-based CAPTCHAs and complex visual layouts.
– **Documentation Drive:** A concerted effort to improve onboarding materials to sustain the influx of new contributors.
**Broader Trends:**
– **Rise of Agent Frameworks:** ClawBot is part of a larger wave of “agent” frameworks aiming to make LLMs actionable.
– **Sustainability Focus:** The community is increasingly scrutinizing the energy efficiency and cost of running AI agents at scale.
– **Regulatory Awareness:** As automation tools become more powerful, discussions around ethical use and compliance are growing within the community.
Conclusion
ClawBot’s ascent to 100,000 GitHub stars demonstrates the power of open-source collaboration in the AI landscape. Its architecture offers a blueprint for building reliable, efficient automation agents that can operate independently of large tech ecosystems.
This milestone likely signals the beginning of a broader trend where individual developers and small teams can successfully challenge established players. The project’s continued evolution will be a key indicator of where the open-source AI agent market is heading.
FAQ
What is ClawBot?
ClawBot is an open-source AI agent designed to automate web browsing tasks. It uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to plan actions and an execution engine to interact with web pages, handling tasks like data entry, navigation, and form filling autonomously.
Why did ClawBot reach 100,000 GitHub stars?
The project reached this milestone due to its practical utility, reliable architecture, and open-source accessibility. It addresses a common need for web automation while offering a transparent alternative to proprietary tools, attracting a large community of developers and automation enthusiasts.
How does ClawBot differ from other AI agents?
ClawBot distinguishes itself through its modular architecture that separates planning from execution. This reduces errors and hallucinations common in direct LLM-to-browser interactions. It is also a solo-developed project, making it a unique case of independent success against corporate-backed competitors.
Is ClawBot free to use?
Yes, ClawBot is open-source and available for free on GitHub. Users can clone the repository and run it locally, though they will need API keys for the underlying LLMs (like GPT-4 or open-source alternatives) which may incur costs depending on usage volume.
What are the technical requirements to run ClawBot?
To run ClawBot, users typically need Python, a compatible browser driver (like Playwright or Selenium), and access to an LLM API. The project documentation provides setup instructions, and it is designed to run on standard consumer hardware for most tasks.
What is the future roadmap for ClawBot?
The developer plans to introduce a plugin system for extensibility, improve multimodal capabilities for visual tasks, and enhance documentation. These updates aim to foster a larger developer community and improve the agent’s ability to handle complex real-world scenarios.













How would you rate Lobster-Inspired AI Clawbot Conquers 100K GitHub Stars?