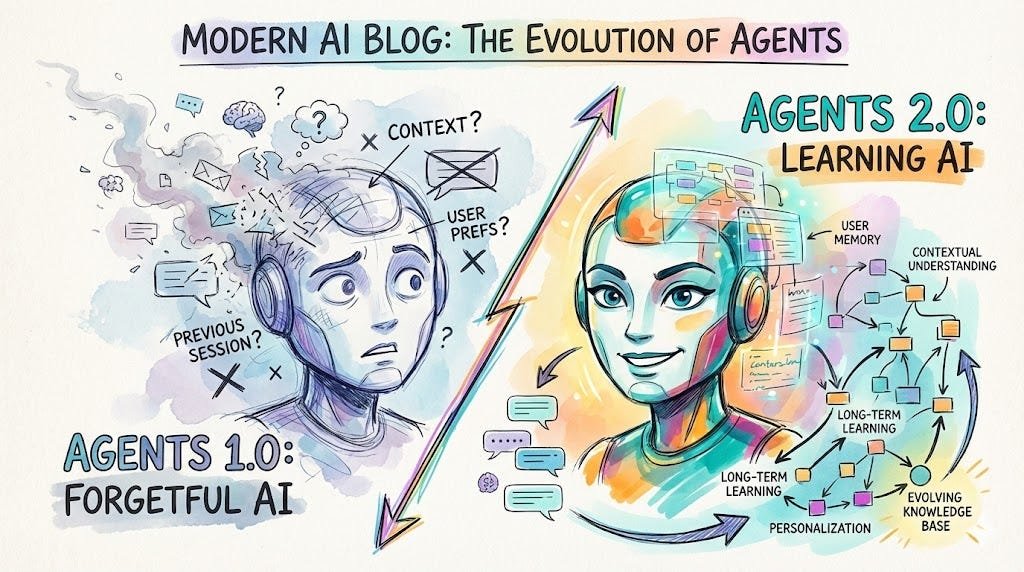
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the concept of “AI Agents 2.0” is gaining significant traction. Unlike their predecessors, which often suffer from amnesia—forgetting user preferences and context from one session to the next—these next-generation agents are designed with persistent learning capabilities. This article explores the six learning types that enable memory persistence, transforming how AI interacts with users and businesses.
The Memory Problem in Traditional AI Agents
Traditional AI agents, including many chatbots and virtual assistants, operate with a limited context window. Once a conversation ends or exceeds a certain token limit, the agent forgets previous interactions. This limitation creates a frustrating user experience, forcing users to repeat information and re-establish context in every new session. For businesses, this means missed opportunities for personalized service and inefficient workflows.
Introducing Persistent Learning: The Core of AI Agents 2.0
Persistent learning refers to the ability of an AI agent to retain and utilize information across multiple sessions. This is achieved through various learning types that store, retrieve, and apply knowledge over time. By integrating these mechanisms, AI Agents 2.0 can remember user preferences, past interactions, and specific instructions, leading to more coherent and personalized interactions.
The Six Learning Types That Make Memory Persistent
To understand how persistent learning works, we must delve into the six fundamental learning types that power AI Agents 2.0:
1. Supervised Learning
Supervised learning involves training the AI on labeled datasets, where each data point includes the correct output. This method allows the agent to learn patterns and correlations, enabling it to predict outcomes based on new inputs. For instance, an AI agent can learn to categorize customer inquiries based on historical data, improving its response accuracy over time.
2. Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning, the AI analyzes unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns and structures. This is particularly useful for clustering similar user behaviors or identifying trends without explicit guidance. For example, an AI agent might group users with similar browsing habits to offer tailored recommendations.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning trains the AI through trial and error, rewarding desirable actions and penalizing undesirable ones. This method is ideal for dynamic environments where the agent must adapt its strategy. In customer service, an AI agent can learn which responses lead to higher satisfaction scores, continuously refining its approach.
4. Semi-Supervised Learning
Semi-supervised learning combines a small amount of labeled data with a large pool of unlabeled data. This approach is cost-effective and efficient, especially when labeling data is expensive or time-consuming. AI agents can use this to improve their performance with minimal human intervention.
5. Self-Supervised Learning
Self-supervised learning generates labels from the data itself, allowing the AI to learn from vast amounts of unstructured information. This method is crucial for building robust language models that understand context and nuance, enabling them to generate more human-like responses.
6. Transfer Learning
Transfer learning leverages knowledge gained from one task to improve performance on a related task. This reduces the need for extensive retraining and allows AI agents to adapt quickly to new domains. For example, an agent trained on general customer service can be fine-tuned for specific industries like healthcare or finance.
Practical Applications and Use Cases
AI Agents 2.0 with persistent learning capabilities are transforming various industries:
- Customer Support: Agents remember past issues and preferences, providing seamless support without repetition.
- E-commerce: Personalized shopping experiences based on previous purchases and browsing history.
- Healthcare: Virtual assistants recall patient history, offering tailored health advice and reminders.
- Education: Adaptive learning platforms that remember student progress and adjust content accordingly.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of AI Agents 2.0 over traditional AI agents?
AI Agents 2.0 offer persistent learning, allowing them to remember user interactions across sessions. This leads to more personalized and efficient experiences compared to traditional agents that forget past conversations.
How does supervised learning contribute to persistent memory?
Supervised learning trains AI on labeled data, enabling it to recognize patterns and make accurate predictions. This helps the agent retain and apply knowledge from previous interactions.
Can AI Agents 2.0 be used in healthcare?
Yes, AI Agents 2.0 are particularly beneficial in healthcare for remembering patient history and providing tailored advice, improving the quality of care.
What industries benefit most from persistent learning?
Industries like customer service, e-commerce, healthcare, and education benefit significantly due to the need for personalized and context-aware interactions.
How does transfer learning enhance AI agent capabilities?
Transfer learning allows AI agents to apply knowledge from one domain to another, reducing training time and improving adaptability to new tasks.










How would you rate Breakthrough AI Agents with Persistent Memory – The Future of AI Interaction?